Data Strategy Roadmap: Creating a Data Strategy Framework For Your Organization
Learn about the benefits of a data strategy roadmap and how to create one. Understand the key elements of a data strategy framework.
Overview of Data Strategy
Today, in a data-driven world, organizations recognize the importance of implementing a well-defined data strategy framework.
A 2023 executive survey from NewVantage Partners reveals that 82.6% of large U.S. corporations have appointed a Chief Data Officer (CDO) or Chief Data and Analytics Officer (CDAO), showcasing continued growth and commitment towards their data investments.
A solid data strategy developed under the leadership of C-suite executives provides a blueprint for efficient enterprise data management and utilization across all systems and teams.
Key Takeaways
- Developing a data strategy roadmap requires aligning data initiatives with business goals and building a data-driven culture.
- Key steps in creating a data strategy roadmap include identifying business challenges, assessing current data resources, forming a data team, and defining key performance indicators (KPIs).
- A data strategy roadmap provides a framework for evolving from ad hoc analytics to a mature data-driven organization through continuous iteration.
What Is a Data Strategy Framework?
Gartner defines data strategy as “a dynamic process used to support the collection, organization, assessment, and data delivery to accomplish the organization’s goals.”
Hence, a data strategy framework is a long-term, comprehensive, and structured data management approach.
It defines the principles, methodologies, processes, technologies, and people required to manage and utilize raw data as a strategic information asset within an organization, helping it to make informed decisions and achieve business goals.
It strives to link an organization’s data initiatives with its business objectives amidst constant change.
As a result, organizations experience a streamlined data architecture, improved operational efficiency, enhanced data integrity/compliance, and higher levels of business innovation.
Importance of a Data Strategy Framework
Organizations without a robust data strategy framework encounter several issues, including:
- Lack of data-driven decision-making, resulting in negative business growth and missed opportunities.
- Data silos and inconsistencies among departments impede collaboration and prevent a comprehensive understanding of the organization's data assets.
- Not being able to use data as a strategic asset hinders innovation and minimizes competitive advantage.
- Severe risk of data breaches, non-compliance with regulations and harm to reputations.
- Not being able to allocate data resources effectively, leading to wastage and data pipeline inefficiencies.

Data Strategy Goals
Data strategy goals encompass the overarching objectives that organizations strive to achieve through effective enterprise data management and utilization.
The following goals are pivotal in shaping an organization's data strategy framework.
Fostering Innovation
By leveraging data assets, an organization’s data strategy should aim to increase data literacy and drive innovation across various operations to increase revenue streams.
This entails creating data-driven products, services+ and processes. Plus, encouraging a data-first culture across teams.
Taking a User-Centric Approach
An organization’s data strategy should enable it to leverage data-driven insights and decision-making to improve user experience and satisfaction, and proactively resolve customers’ issues by offering custom solutions.
Managing Risks & Compliance
When organizations build a data strategy and governance framework, they must ensure data security, privacy, confidentiality of sensitive data, and compliance with regulatory frameworks across all organizational data assets.

Six Major Benefits of a Well-Defined Data Strategy
A well-defined data strategy offers organizations many benefits, enabling them to manage and utilize their data assets effectively in order to maximize business value. Some major benefits include:
1. Providing a Competitive Advantage
As a strategic asset, data offers organizations a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving marketplace. It enables businesses to discover emerging trends and opportunities within their proprietary customer data.
They can make informed decisions related to unique product improvements based on data-driven insights. As a result, organizations are better equipped to satisfy customers and attract prospects compared to their competitors.
2. Improving Decision-Making
A Salesforce survey conducted in September 2023 shows that 73% of data leaders agree that data reduces uncertainty, leading to more accurate decisions in business conversations.
Decision-makers like C-suite executives and board members can leverage data-driven analytics and insights to assess their organization's performance, understand customers' preferences, and grasp market dynamics.
By implementing a robust data stragy and increasing data literacy, executives are enabled to make quick and accurate decisions.
3. Increasing Efficiency & Productivity
A well-defined data strategy streamlines data operations, boosting the organization’s productivity and efficiency. In fact, 72% of business leaders globally believe that data keeps employees focused on relevant and high-priority business aspects.
Organizations can decrease manual and repetitive operations, reduce errors and free up resources by utilizing data integration and automation pipelines. As a result, data teams can concentrate on higher-value tasks, encouraging further innovation.
4. Aligning Data Management Efforts With Business Objectives
An effective data strategy creates a structure for collecting, storing, and analyzing data while ensuring that enterprise data management initiatives align with the organization's goals.
Moreover, it breaks down data silos by promoting integration and collaboration across departments.
5. Compliance
In this age of cybercrime, part of a well-defined data strategy includes initiatives to ensure adherence to data privacy, relevant legislation, and industry standards and bast practices.
Major data regulatory compliance frameworks, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA set guidelines for handling personal and sensitive data.
Businesses must protect the sensitive data of their customers in order to uphold their trust, and they can face serious financial consequences in the case of a data breach.
According to an IBM report, the average cost of a data breach reached $4.35 million in 2022. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences, including reputational damage, financial penalties and legal ramifications.
6. Future-Proofing
Data strategy aids organizations in future-proofing their operations, by enhancing their data-driven capabilities.
Organizations can leverage advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning to obtain deeper insights from their customer data to unlock new opportunities.
Data leaders are using decision intelligence, which is based on advancements in data science and behavioral science to make resilient business decisions at any scale. It makes them agile and adaptable to changing consumer preferences and market trends.
Hence, by investing in their data strategy, organizations can tap into the full potential of their data assets, and drive sustainable growth in today's data-driven landscape.

The Elements of Data Strategy
Typically, a robust data strategy consists of four key components that collectively contribute to its effectiveness in driving organizational success:
1. Business Strategy
In data-driven organizations, data strategy and business strategy are tightly coupled. Hence, your data initiatives must align with your business goals. So how can we define such a data strategy?
- Start by understanding and documenting stakeholder (mainly customers and executives) requirements.
- Assess your existing data infrastructure and processes, and understand your data maturity level. This evaluation provides a basis for creating a data strategy that aligns with business objectives.
- Finally, establish short-term and long-term data strategy goals, and quantifiable objectives aligned with business requirements. For instance, a short-term goal can be to update the backups of processed business data every week, while a long-term goal can be to increase business ROI by 10% in the next two years based on current data investments.
2. Organizational Roles
The organization's roles and responsibilities must be clearly defined to implement your data strategy successfully.
Finding data stewards, data owners, data managers, data analysts, data engineers, data architects, and other specialized resources is a crucial part of this process.
A well-defined data strategy promotes a culture of data governance to ensure that data-related activities are well-coordinated and successfully carried out under the direction of a CDO/CDAO by relevant data teams and resources.
3. Data Architecture
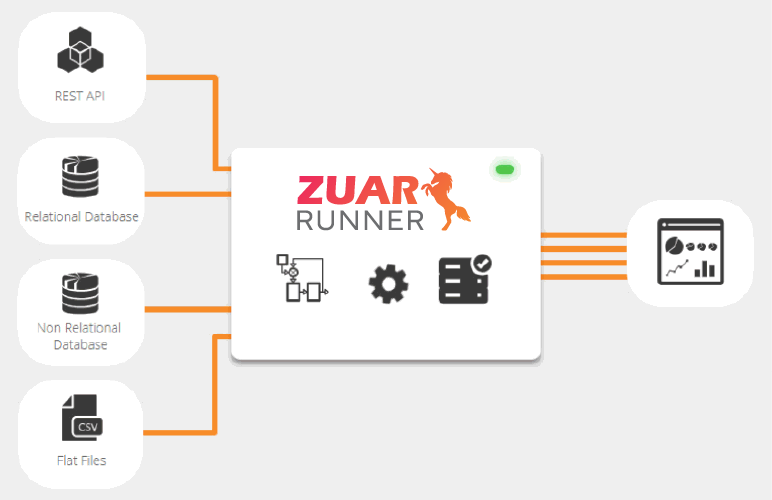
A well-defined data strategy encompasses the design of a robust and modern data architecture that considers various aspects, including data sources, destinations, and processing infrastructure.
For instance, organizations can choose between data warehouses or data lakes, or both as storage options. They can also choose to implement data fabric or data mesh architectures to streamline data pipelines across all teams and systems.
They can also leverage data catalog and metadata management tools to streamline their data assets. As a result, businesses ensure effective data flow, integration, and processing.
Furthermore, a sound data architecture makes it easier to generate advanced analytics and insights, allowing businesses to extract useful information from their data assets that spur innovation and corporate growth.
4. Data Management
A comprehensive data strategy also includes data management, consisting of diverse procedures, including but not limited to:
- Data Virtualization: Enables teams to quickly get a virtually holistic view of organizational data spread across departments. For instance, the marketing team can virtually gather sales and customer support data to create more informed marketing campaigns.
- Data Democratization: Empower teams with data access across organizations and promote a data-driven culture. This means everyone should be comfortable with business data regardless of their technical expertise. A platform like Zuar can simplify data democratization.
By integrating these four elements into a cohesive data strategy, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data assets.
This holistic approach enables organizations to align data initiatives with business objectives, design robust data architectures, and implement effective enterprise data management practices.

Eight Steps to Create a Robust Data Strategy Framework for Your Organization
By following the steps given below, organizations can lay the foundation for effective data management, align data initiatives with business goals, and position themselves for success in this digital age.
1. Identify Key Stakeholders
Start by identifying key stakeholders related to your data investments. Typically, these are your customers, C-suite executives and data teams. Each would have their distinct input on organizational data initiatives.
For instance, on the customer end, it is important to build data products that represent each customer group. Understanding their views and opinions and collecting relevant data is extremely important. Otherwise, your products and services can be biased against underrepresented groups.
Hence, a successful data strategy roadmap depends on incorporating your stakeholders' unique viewpoints and expertise into business processes. This provides them a sense of ownership, which enhances stakeholder empowerment and increases the likelihood of implementing and adopting the data strategy successfully.
2. Discovery
This step involves defining key business drivers and desired outcomes that the data strategy aims to support.
Department heads or managers usually define objectives and key results (OKRs) for a planning period. Objectives are often governed by SMART principles (i.e., Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound).
A targeted data strategy that meets specific business needs and creates value is easier to build when the organization's data objectives are clearly understood.
For instance, an organization can choose to define which data lineage tools, metadata management tools, and data catalog tools will be used to minimize uncertainty and instill trust in data. Or they can choose to build a unified/centralized data ecosystem that will eliminate silos and empower internal team communication.
Companies can also define a data analytics strategy as part of their organization’s data strategy to extract deeper insights from their data.
In addition to empowering decision-making processes that align with the larger organizational strategy, it lays the groundwork for exploring data as a strategic asset.
3. Audit Existing Technology Stack & Data Platform Architecture
In this step, organizations conduct assessments to evaluate the capabilities and effectiveness of their existing technology stack, including their data architecture, data management components, and storage technology.
To facilitate seamless data flow between systems, identifying data integration and migration capabilities is essential. The evaluation also considers infrastructure aspects like usability, security, compatibility and scalability.
This assessment ensures that teams are well aware of the capabilities and costs of the current stack, and are able to expand it according to the organization's data strategy.
4. Define Key Performance Indicators
When evaluating the effectiveness of an organization's data management initiatives, key performance indicators (KPIs) are extremely important in answering analytical questions. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
KPIs are used as comparison points to assess the effectiveness and progress of data initiatives. Organizations can identify various areas of development, such as data quality, data integration, data storage and data delivery; then set relevant KPIs that align with business objectives.
For instance, if we only list prominent data management KPIs, then organizations must have processes in place to monitor the uniqueness, availability, completeness, and consistency of data to ensure high-quality data pipelines.
The relevant teams collect data for each KPI and their values are evaluated after specific intervals. Hence, by monitoring and evaluating KPIs, organizations can make data-driven adjustments and ensure their data architecture’s success.
5. Data Governance
This step involves outlining a comprehensive data governance policy encompassing key aspects such as data quality standards, auditability, transparency, stewardship, standardization, privacy regulations and security protocols.
Organizations should establish clear accountability for data-related decisions and actions by defining data governance roles and responsibilities.
Some core data governance capabilities include:
- Ensuring data access is secure and only available to relevant stakeholders (user permission and rights management).
- Designing a systematic framework for classifying and managing data assets.
- Creating a centralized repository for managing data assets via data catalog, and metadata categorization based on attributes.
- Monitoring the origin, modifications and migration of data via data lineage tools to guarantee accuracy and compliance.
- Establishing a single, accurate, consistent version of data by minimizing data silos across the organization to enable and empower data democratization.
6. Organizational Structure
This step involves designing a team structure that facilitates cross-functional collaboration and establishes clear roles and responsibilities.
A typical team structure starts with a CDO, CIO, or CTO, followed by VPs or directors of engineering and operations who lead teams of various data-specific roles like solution architects, implementation architects, data engineers, data scientists, DevOps engineers, etc.
Organizations can improve collaboration and knowledge sharing by filling any skill shortages and establishing these specialized data teams capable of executing short sprint cycles with achievable milestones. This allows them to plan strategically, validate concepts, and gradually scale the initiatives for maximum impact.
7. Implementation Plan
A typical data strategy implementation plan includes designing, data processing, use case development, testing/validation, deployment, monitoring and upgrades.
It also includes setting realistic timelines and budget allocations for each phase of the transformation roadmap. Moreover, to guarantee a seamless implementation, organizations must develop a communication strategy.
8. Continuous Review & Updates
The final step involves continuously reviewing and updating the data strategy roadmap. Organizations can maintain alignment with changing business requirements and adopt new technologies as they emerge by routinely examining the data roadmap. Additionally, it offers a chance to modify the plan in light of lessons learned and stakeholder feedback.
By embracing a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can guarantee that their overall digital roadmap, including their data strategy, remains relevant, efficient and flexible in the face of shifting business environments and technology breakthroughs.

Data Strategy Next Steps
Building a comprehensive data strategy roadmap can be intimidating as it involves a lot of complexities related to data, engineering and operations. Zuar can help.
Our team of experts is here to guide you every step of the way, from stakeholder identification to implementation and optimization. We'll help you navigate through the complexities of data automation/pipelines, data governance, analytics dissemination, and more.
Let the experts at Zuar clear a path towards the implementation of an amazing data strategy for your organization: