What Is a Data Portal? Everything Explained
Are you looking to understand data portals? In this complete guide, see what they are and the different kinds- vertical, horizontal, marketplace, media, etc.

In today's data-driven world, information is king, and access to the right data can make all the difference in decision-making, innovation, and progress.
But with the ever-increasing volume and complexity of data, finding, organizing, and extracting valuable insights from this wealth of information can be a daunting task. That's where data portals come into play.
Imagine having a single, user-friendly gateway that grants you access to a treasure trove of data from various sources, all neatly organized, and ready for exploration.
This is the promise of data portals, and in this article, we'll embark on a journey to explore these valuable tools that have transformed the way we interact with data.
Whether you're a data enthusiast, a business leader, a researcher, or simply curious about the possibilities of data, this article will show you how data portals can be your compass in the vast sea of information, helping you navigate and harness the power of data for informed decision-making and beyond.
Related Article:

What Is a Data Portal?
A data portal is a web application, website, or page of a website that holds data from different sources, organized under subsets or categories to make it simple for the site's users to find.
Data portals typically offer tools for searching, filtering, and downloading datasets, often in various formats, allowing users to explore and utilize data for research, analysis, policy-making, application development, and more.
The aim of a data portal is to facilitate the discovery and utilization of data, fostering innovation, transparency, and collaboration.
Users should be able to access a data portal easily, no matter what device they are using (desktop, tablet, or smartphone).
Some of the key components of data portals include:
- Data Access: Data portals provide a central repository for various types of data, including structured and unstructured data, such as databases, spreadsheets, text documents, and more. Users can access this data through a user-friendly interface.
- Data Exploration: Users can explore and search for specific datasets and data sources within the portal. This includes the ability to browse metadata, data descriptions, and data dictionaries to understand the content and context of the available data.
- Data Integration: Data portals often allow users to integrate data from multiple sources, creating a unified view for analysis. This integration may involve data transformation, cleansing, and enrichment to ensure data quality.
- Data Organization: Data is organized in a structured manner, making it easier to find and work with. Users can typically navigate through categories, tags, or keywords to locate relevant datasets.
- Collaboration: Many data portals support collaboration features, allowing multiple users to work together on data analysis and share their findings with colleagues. This fosters teamwork and knowledge sharing.
Types of Data Portals
There are several types of data portals, each designed to serve different purposes. Here are some common types:
Analytics Portal
An analytics portal is a specialized platform or tool designed to facilitate the discovery, access, and analysis of data for the purpose of generating insights and making data-driven decisions within an organization.
These portals are typically used by organizations and individuals who require access to data for business intelligence, data analytics, and reporting purposes.
By having all of the company's data insights centralized in a single location, there is no longer any need to switch between various applications trying to find the data you need.
Zuar Portal is an example of an analytics portal that is fully customizable with drag-and-drop simplicity. By implementing this solution, organizations can provide all stakeholders with a one-stop shop for all their business intelligence in an easily digestible format.
Intranet Portal
Your business's internal data, apps, and information can be managed quickly and conveniently with an intranet portal.
Features such as calendars, workflows, targeted content, blogs, and other operational tools will allow your teams to find the right information, improve their communication, and be more productive.
These portals will also be an effective accessible place when dealing with customers through any multichannel contact center.
Open Data Portal
Open data portals are platforms that provide free and open access to a wide variety of data, typically collected and maintained by government agencies, non-profit organizations, or other entities.
These portals aim to promote transparency, accountability, and innovation by making data available to the public for analysis, research, and application development.
For example, this open portal from iFremer, a French research institute, is used to observe the status of the marine and maritime environment.
Government Data Portal
A government data portal is a type of open data portal specific to government entities, such as national or local governments. They offer access to a wide range of government-related data, including demographic information, public finances, environmental data, and more.
These portals are often used to facilitate government transparency and provide data for decision-making.
Data.gov is an example of a government portal run by the United States federal government that aims to make itself more open and accountable.
What Are the Primary Advantages of a Data Portal?
A data portal collects information from different sources into a single user interface to present the most relevant information, making it easy for users to find content and applications in one place.
A data portal unifies information in a personalized way, integrates all your disparate systems into one UI, and helps you build sophisticated websites or web applications quickly.
Many great features can be built into a data portal that makes developers' and customers' lives easier:
- A data portal creates a framework that helps developers easily add components without needing to write each piece from scratch.
- Data portals create a one-stop shop for all the important information and visualizations that stakeholders need.
- A workflow-enabled data portal can function as a web content management system, often including related utilities such as video embedding and a basic photo editor. Certain portals can also seamlessly integrate video-related content, powered by AI video generator tools, to enhance your business operations.

What is a Modern Data Portal?
Modern data portals can be private-facing or public-facing applications built to allow end users to explore, interact with, and derive intelligent insights from data in order to perform a task or answer a question.
Modernized data portals build upon many of the previously mentioned attributes to formulate what would ultimately be considered a data application or centralized place for all of your data, visualizations, insights, and related content.
The framework for a modern data portal should allow users to set up live connections to data sources (or databases), like MySQL, Microsoft Access, Snowflake, Exasol, etc.
After connecting, users are able to leverage data visualization or embedded analytics tools to perform complex data analyses.
Components of a Modern Data Portal
A modern data portal should allow businesses to build a Data Value Chain to turn data into actionable insights, use it to gain a competitive advantage, or monetize it.

A modern data portal should consist of 5 major components:
- Data Source(s): Modern data portals should have a user-friendly way of establishing secure, live connections to data sources or databases, directly from the UI. Seamless integration with data sources is crucial for an efficient workflow, eliminating the need to juggle multiple applications solely for connecting to diverse databases.
- Query Building: A user-friendly way of writing queries against the data source to compute, aggregate, transform, build views, and extract data from the database for analysis.
- Data Visualization: It is an undisputed fact that visualizing data allows you to unlock key insights to make data-driven decisions. Modern data portals should have a way to build data visualizations off of the data queries.
- Access Control: Access control within data portals is pivotal for ensuring the security, integrity, and confidentiality of stored information. Restricting access to authorized users prevents unauthorized entry or modification of sensitive data, complying with legal regulations and internal policies.
- Branding and Design: Modern data portals should be fully customizable from the web, allowing you complete control over branding, layouts, design, color palettes, typography, etc. Modern data portals have drag-and-drop functionality and the ability to write custom front-end code with HTML, CSS, and JS.
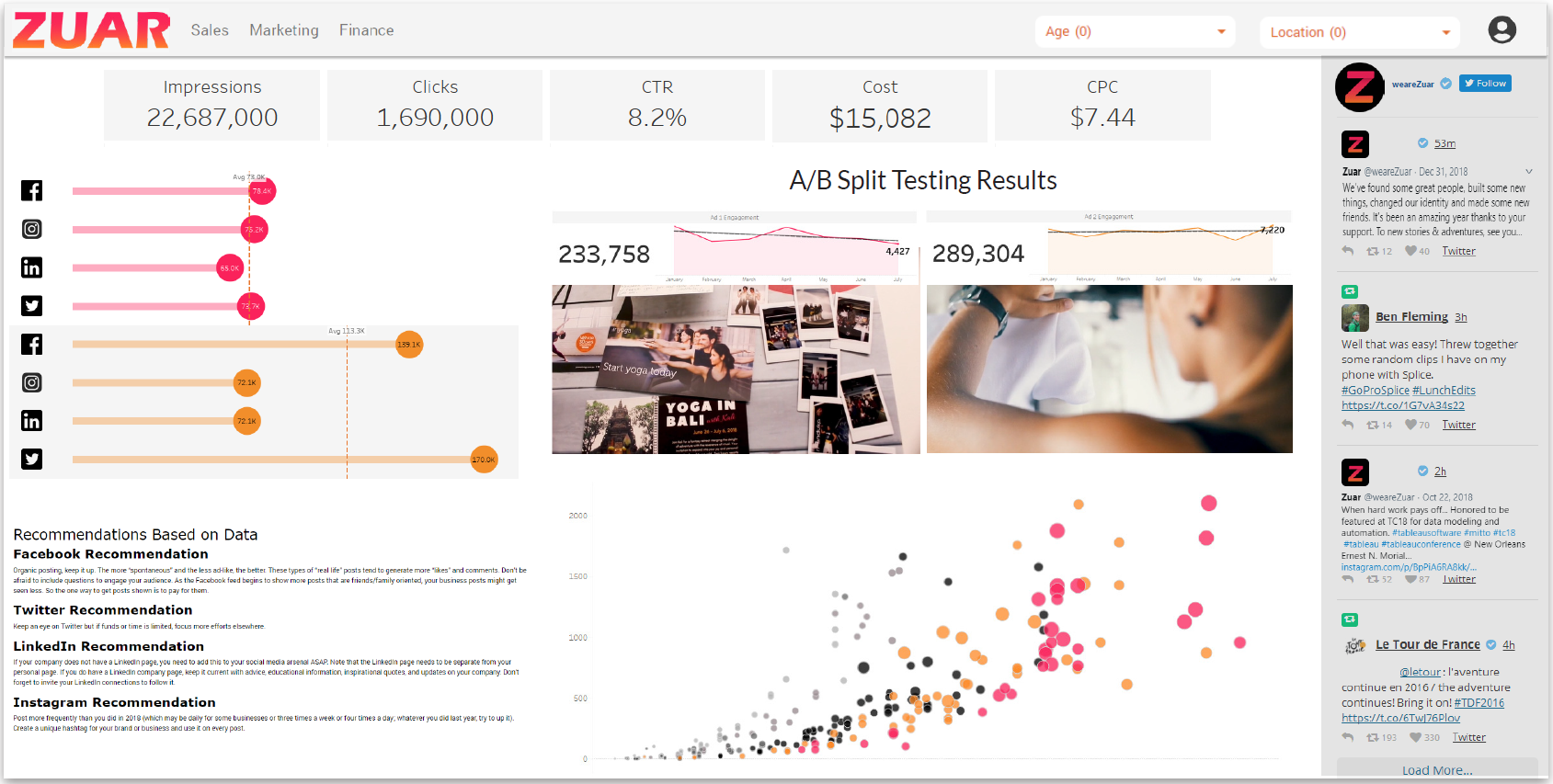
Differences Between Traditional and Modern Data Portals
Traditional data portals and modern data portals have many similarities, as highlighted above, but also some key differences.
Control Over the Entire Data Pipeline
Modern data portals emphasize the importance and accessibility of data and data-driven insights. After all, this is a "data" portal.
Instead of relying on multiple layers of sophisticated technology or a web application, a modern data portal is all-inclusive. This allows end users full control of their data pipeline, data input or write back, database, analytics, data visualizations, users, and content all in one place.
Dynamic Behavior and Interactivity
In essence, if you see an interesting data point, you should be able to drill in further until you reach the required level of granularity to answer a question or solve a problem.
Interactive components in a portal can facilitate this process. For example, a marketing director is analyzing lead acquisition data and sees a jump in leads during a day in August.
The director selects the data point, which filters surrounding visuals and content to discover a majority of those leads came from LinkedIn. They drill in further to discover that a member of the sales team shared a how-to video about one of their new product features.
With one last click, the marketing director is able to see the exact videos shared on that particular day and compare the performance of each while also being able to watch the video in the portal! The director now has a strategy for future lead acquisition supported by data.
A Guided Experience to Drive Insights
In the modern world, business decisions need to be made quickly and accurately. A contemporary data portal accelerates the process of extracting value from the data it houses, enabling users to efficiently balance their various job responsibilities without prolonged focus on data handling.
It does this by guiding the user to the answers they're seeking via interactive content, navigation, and custom workflow.
What's Next
Data portals offer organizations a powerful tool for harnessing the full potential of their data assets.
By understanding the different types of data portals, their key features, and the numerous benefits they offer, organizations can make more informed decisions, drive innovation, and foster a data-driven culture.
But which data portal solution should you choose? We recommend Zuar Portal.
Zuar Portal
If you are interested in learning more about modern data portals, Zuar is ready to help. Zuar Portal allows you to create curated analytics experiences for all of your data customers. The key features of Zuar Portal are that it:
- Allows you to build your analytics headquarters by moving beyond stand-alone dashboards. Combine data visualization with multi-media, data tables, and any web-based information while allowing dynamic interaction between all the content.
- Helps simplify and focus your content. Rather than sorting through a myriad of content, surface exactly what your users want to see—guided by custom navigation.
- Allows you to fully customize your experience with drag-and-drop simplicity. Universal web languages (CSS, HTML, JS) give you complete control to customize everything from branding and styling to user interaction.
- Monetize your data. Build your own data portal and sell your insights! Create a custom-branded experience and turn your valuable data into a source of revenue.
Turn this vision into your reality by scheduling a demo with one of our friendly data experts! We can quickly spin up a Zuar Portal demo that incorporates your company's branding and pulls data from all your data sources.
Learn firsthand how Zuar Portal can revolutionize the way you disseminate your data insights.




