Unlocking the Value of Industrial Data
In this guide, we'll take a deep dive into the world of industrial data—highlighting the best tools and methods for collecting and analyzing it with the goal of increasing efficiency and driving revenue.
Enterprises gather an ocean of industrial data, yet often a majority of that data goes unused. Within this underutilized data lies the key to revolutionizing efficiency, cost-reduction, and decision-making in manufacturing.
This article will detail what constitutes industrial data, its transformative role in businesses, strategies for its collection and analysis, and the innovations making use of every byte.
What Is Industrial Data?
Industrial data refers to the collection of information generated from activities within industrial settings, including manufacturing, logistics, energy production, and other sectors involved in the production and distribution of goods and services.
Industrial data carries tremendous potential value, yet a significant portion of it remains untapped. Estimates suggest that between 60% to 73% of the data gathered by enterprises remains unused, signifying a vast treasure trove of potential insights yet to be discovered.
But what role does industrial data play in manufacturing processes, and how is it collected and stored? Let’s examine this in more detail.
Defining Industrial Data
Industrial data encompasses a wide array of types, such as machine performance metrics, production output statistics, quality control measures, equipment maintenance records, and environmental conditions.
But merely having raw data isn’t enough. The true value lies in the insights derived from this data.
Interpreting industrial data correctly can aid in management decision-making, reduce maintenance expenses, and enhance customer service.
By analyzing machine, personnel, and production data, manufacturers can identify patterns and trends that can lead to more efficient processes, higher quality products, and ultimately, a healthier bottom line.
In an era where efficiency is king, the power of data is a game-changer.
Collecting and Storing Data: Methods and Best Practices
Given the significant role of industrial data in manufacturing, it’s natural to question how this data is gathered and preserved.
The answer lies in robust systems, best practices, and secure storage solutions. Industrial data processing involves the collection, storage, and analysis of data, typically on a large scale across an enterprise.
In the past, production data was gathered using proprietary terminals, and then transmitted to a central database-based system that was locally installed.
Today, we have Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), which extend beyond the capabilities of a standard production data collection system, encompassing features such as blocking process steps and guaranteeing traceability.
And while the methods of collecting data have evolved, one thing remains constant - the need for secure storage. Ensuring strong security is a vital consideration to safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of the collected production data.
Check out our webinar on indutsrial analytics for a deeper dive into this topic:

Tools for Industrial Data Collection and Analysis
There are many types of tools and systems that industrial companies can implement to optimize data collection and analysis.
We'll now take a deep dive into two main categories of industrial data tools: information technology (IT) systems and operational technology (OT) systems. We'll also provide examples of vendors who provide them.

Operational Technology (OT) Systems
OT systems consist of specialized hardware and software designed to monitor, control, and ensure the efficient operation of industrial equipment and processes.
Here are some OT examples:
- SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) Systems: These are crucial for real-time data acquisition, monitoring, and control of industrial processes across various locations. Examples include Siemens AG and Rockwell Automation
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers): PLCs are used for automating machinery and industrial processes, offering precise control and operational efficiency. Siemens SIMATIC S7, as well as Allen-Bradley ControlLogix, stand out as two top PLC solutions.
- DCS (Distributed Control Systems): DCS are employed for controlling complex, large-scale industrial processes, providing a more integrated approach to process management. Examples include Honeywell Experion PKS and ABB Ability System 800xA.
Information Technology (IT) Systems
While OT systems are dedicated to controlling and monitoring physical devices and processes within industrial environments, Information Technology (IT) systems focus on data management and information flow within an organization.
IT systems are used to manage data, integrate business processes, and support decision-making, facilitating efficient operations and strategic planning across the manufacturing enterprise.
Here are some examples of IT systems:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: These systems integrate key internal business processes, often including inventory management, accounting, human resources, and more, providing a holistic view of the business operations. Two of the largest players in the ERP market are SAP and Oracle.
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): MES bridges the gap between the shop floor and enterprise-level IT systems, managing and monitoring manufacturing information in real time to optimize production. Siemens Opcenter Execution and Plex Smart Manufacturing Platform are two examples.
- Data Analytics and Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: These tools analyze large volumes of data to extract actionable insights, supporting strategic decision-making and operational improvements. We'll detail below how Zuar's industrial solutions can be pivotal in transforming raw industrial data into meaningful and useful information for business analysis purposes.
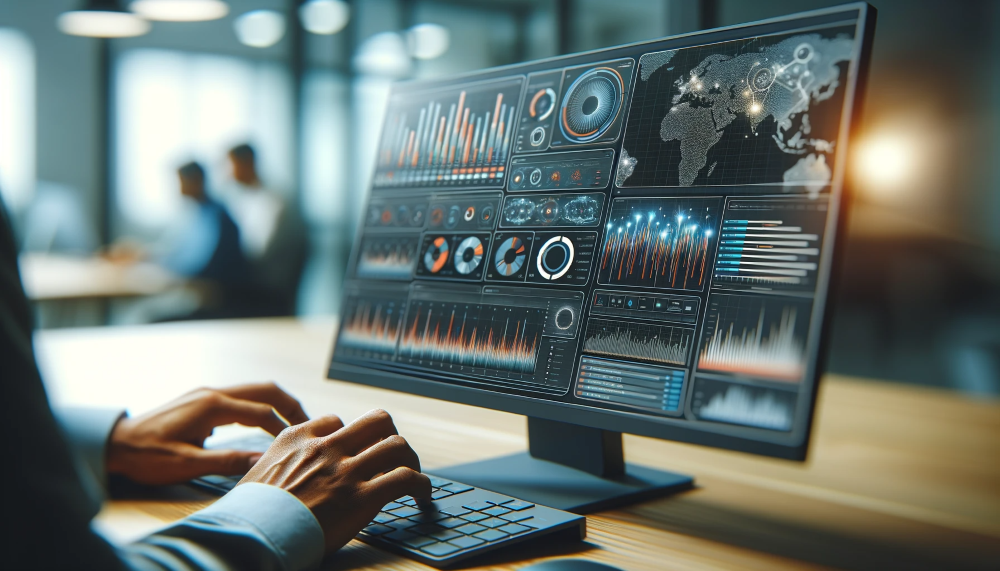
Zuar's Industrial Analytics Solutions
Zuar Runner and Zuar Portal offer comprehensive solutions for enhancing industrial data management and analysis.
Zuar Runner automates the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data from various industrial sources into centralized systems, ensuring timely and accurate data availability.
Meanwhile, Zuar Portal provides a one-stop shop for data analytics and visualization, enabling the easy creation of insightful dashboards and reports on manufacturing processes, efficiency, and performance metrics that can be securely shared with both internal and external stakeholders.
Click here to try out the demo, or to explore more advanced features, start a free trial by clicking here!
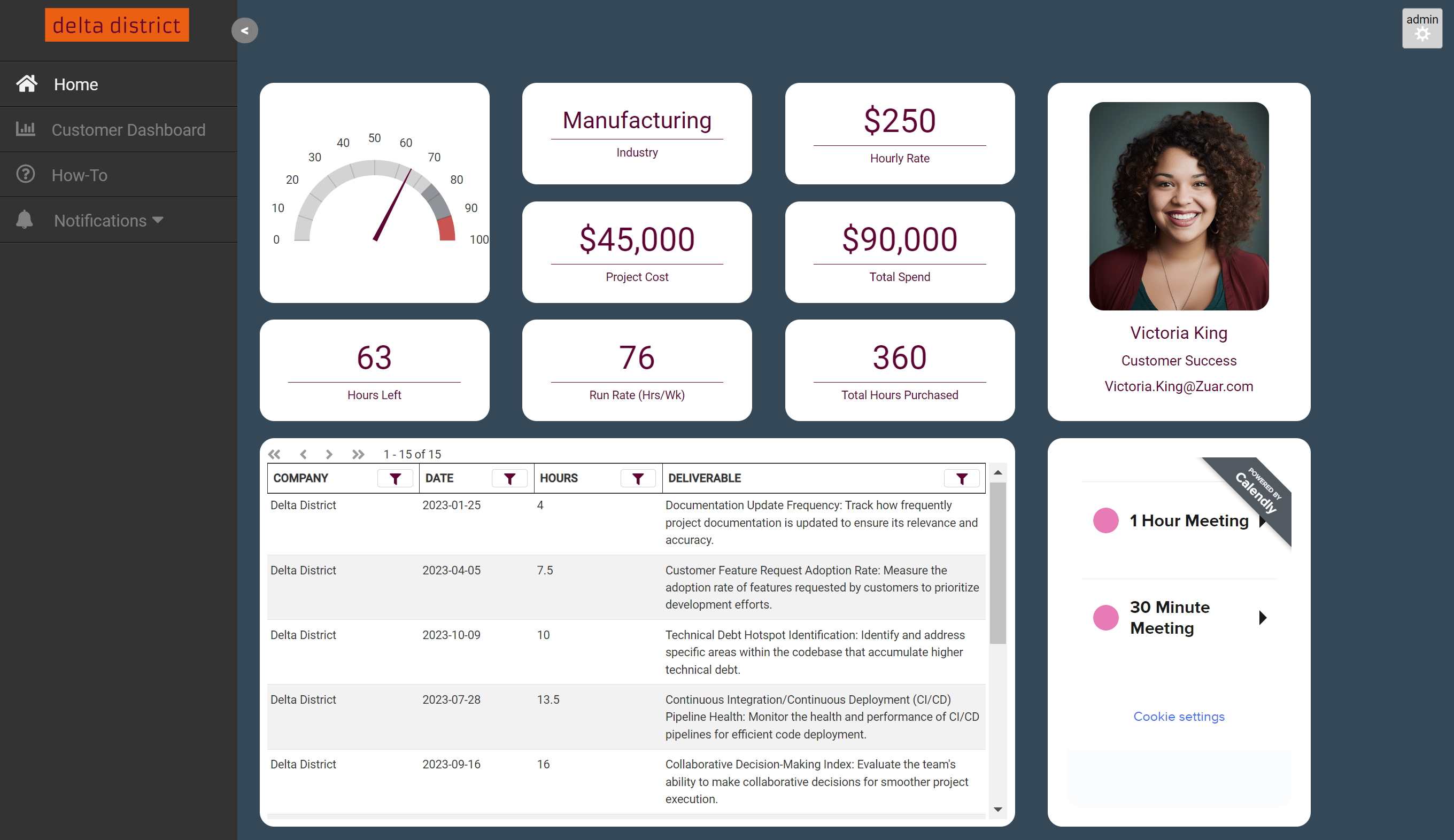
Together, these tools streamline the entire data pipeline, from collection to actionable insights, facilitating improved operational efficiency, decision-making, and optimization in manufacturing environments.
Learn more about Zuar's industrial solutions:


Industry 4.0: Revolutionizing Industrial Data
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, or Industry 4.0, marks a significant transformation in the way industries operate, driven by digitalization and connectivity.
When it comes to industrial data, industry 4.0 signifies a transformative phase where automation, data exchange, and manufacturing technologies converge, enabling highly integrated operational environments.
Internet of Things (IoT)
At the heart of this revolution is the Internet of Things (IoT), a network of interconnected devices and systems that communicate and exchange data with each other and with centralized systems.
This integration has a profound impact on the generation, collection, and utilization of industrial data, setting a new benchmark for operational efficiency, innovation, and sustainability in the industrial sector.
The IoT enables the real-time collection of industrial data from a multitude of sensors and devices deployed across various stages of the manufacturing process, supply chains, and product lifecycle.
This industrial data provides unparalleled visibility into operations, from the performance of a single machine component to the efficiency of entire production lines.
By harnessing this information, businesses can leverage advanced analytics, machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence to identify patterns, predict equipment failures before they happen, optimize processes, and customize production based on specific requirements.
Learn more about visualizing IoT data:
Holistic View of Operations
Industry 4.0 fosters a more integrated and agile approach to manufacturing and industrial practices.
It breaks down silos between OT and information technology IT, facilitating a seamless flow of information across different levels of the organization.
This convergence enables decision-makers to have access to a holistic view of their operations, enhancing their ability to make informed decisions rapidly.
The symbiosis of Industry 4.0 and the IoT heralds a new era in industrial data management. By transforming how data is collected, analyzed, and acted upon, industries can achieve higher levels of productivity, flexibility, and resilience.

Artificial Intelligence: A Game-Changer for Industrial Data Analysis
As we delve deeper into the territory of industrial data, we encounter a powerful ally: artificial intelligence. AI is revolutionizing industrial data analysis by:
- Facilitating predictive maintenance to reduce downtime and costs
- Improving quality control for greater product uniformity
- Offering valuable insights that enable business leaders to make data-driven decisions.
Let’s explore further the transformative capacity of AI.

AI in Predictive Maintenance
AI-powered predictive maintenance systems enhance the lifespan of equipment by identifying issues at an early stage and implementing proactive measures to avert breakdowns, leading to heightened equipment reliability and longevity.
By utilizing AI tools and tools designed to manage and analyze maintenance-related data, manufacturers can reap the benefits of reduced downtime and improved efficiency.
The impact of this can be substantial. By predicting and preventing equipment breakdowns before they occur, manufacturers can ensure the continuity of their operations, minimize disruption, and ensure the steady flow of production. This is just one of the ways AI is revolutionizing industrial data analysis.
Enhancing Quality Control with AI
Quality control is a critical aspect of any manufacturing process. AI contributes to the improvement of quality control in industrial processes by utilizing smart cameras and AI-enabled software to identify product defects and recognize patterns, leading to enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and overall decision-making.
This isn’t just a theoretical benefit. In fact, AI-powered solutions have been shown to assist manufacturing companies in improving yield by up to 30%. AI systems consistently surpass manual testing processes and have the capability to:
- Identify patterns and anomalies in production data
- Predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively
- Optimize production schedules and minimize downtime
These capabilities of AI can greatly enhance the efficiency and productivity of manufacturing operations.
AI-Powered Insights for Business Leaders
While AI can streamline processes and improve efficiency, it also has the power to provide invaluable insights to business leaders.
AI leverages machine learning and data analytics to sift through industrial data, uncovering trends and anomalies that inform strategic decisions, from optimizing production lines to reducing operational costs.
These insights enable business leaders to make informed decisions, enhancing operational efficiency and driving innovation.

Safety and Sustainability: Prioritizing Human and Environmental Health
As we approach the conclusion of our journey through the territory of industrial data, it’s imperative to remember two crucial aspects: safety and sustainability.
In our relentless pursuit of efficiency and productivity, we must never lose sight of the importance of safety protocols and environmental performance. Fortunately, data can help manufacturers prioritize both human and environmental health.
Data-Driven Safety Protocols
Through the use of wearables and data analytics, data-driven safety protocols can effectively incorporate safety measures, identify potential hazards, assess risks, and encourage favorable behavioral changes.
By utilizing this data, manufacturers can proactively identify and address issues, thereby minimizing the likelihood of accidents and ensuring worker safety.
By prioritizing safety, manufacturers can ensure that their quest for efficiency never comes at the cost of human health.
Measuring and Improving Environmental Performance
Just as data can help ensure worker safety, it can also play a key role in measuring and improving environmental performance. By establishing environmental performance indicators (EPIs), manufacturers can work towards minimizing their environmental impact. Such factors include:
- Energy consumption
- Water usage
- Waste generation
- Air emissions
- Supply chain sustainability
The analysis of industrial data aids in the management of environmental impacts, with a generally positive correlation between environmental and financial performance.
In other words, being environmentally responsible isn’t just good for the planet - it’s also good for business.

Industrial Data Next Steps
In the rapidly evolving landscape of Industry 4.0, the management and analysis of industrial data have become pivotal to operational excellence and competitive advantage.
As organizations seek to harness the full potential of their industrial data, the need for comprehensive, scalable, and secure data solutions has never been more critical.
This is where Zuar Labs steps in, offering a suite of cutting-edge data services designed to empower businesses in their digital transformation journey.
We help businesses seamlessly integrate advanced data management and analytics into their industrial operations, leveraging the power of Industry 4.0 technologies to achieve new levels of productivity and innovation.
Whether it's through streamlining data workflows, enhancing data security, or providing strategic insights, Zuar Labs is here to transform your industrial data into a strategic asset for sustainable growth and success.
Learn more by talking to one of our friendly data experts!


Frequently Asked Questions
What is industrial big data used for?
Industrial big data is used for predictive maintenance, production planning, material requirements planning, improving operations, customer service, marketing campaigns, and decision-making to reduce costs and improve productivity.
What is the purpose of production data?
The purpose of production data is to directly assign costs to the factors that incur them, leading to greater cost transparency and improved monitoring and cost management.
How can real-time data enhance manufacturing processes?
Real-time data in manufacturing can improve production monitoring, response times, and efficiency, leading to reduced operational downtime and enhanced product quality.



